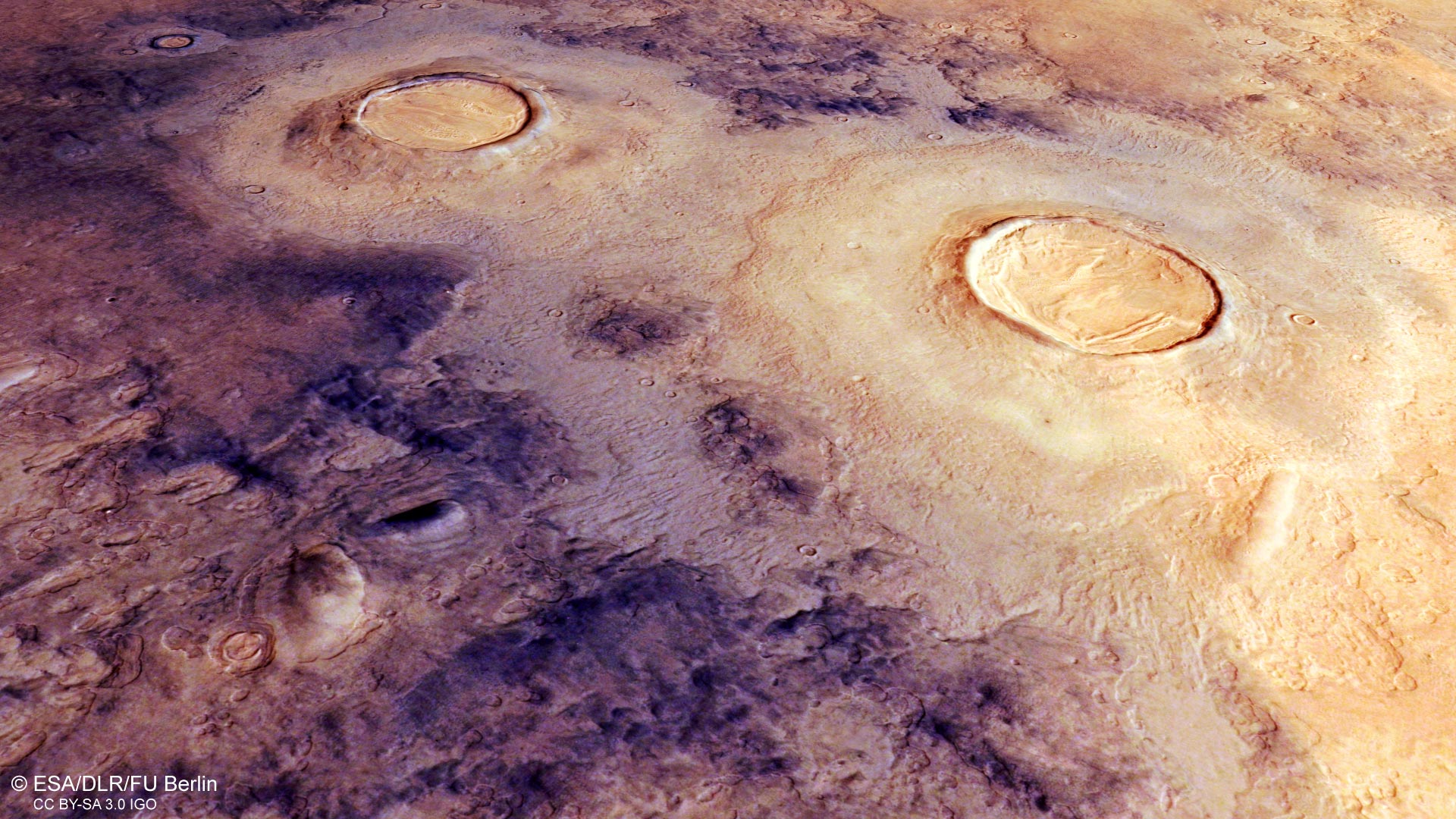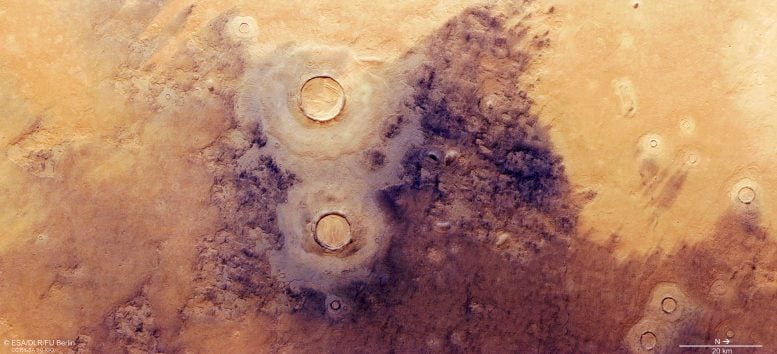
Esta imagen del Mars Express de la ESA muestra Utopía Planitia, una llanura que llena una de las tres principales cuencas del hemisferio norte de Marte -Utopía- y tiene un diámetro de 3.300 km. Esta imagen incluye datos recopilados por la cámara estéreo de alta resolución (HRSC) de Mars Express el 12 de julio de 2021. Crédito: ESA/DLR/FU Berlín, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Nuevas vistas de la ESA[{» attribute=»»>Mars Express reveal fascinating ice-related features in Mars’ Utopia region – home to the largest known impact basin not only on the Red Planet, but in the Solar System.
Utopia is one of three major basins in Mars’ northern hemisphere (along with Acidalia and Arcadia) and has a diameter of roughly 3,300 km: just under twice the north-south size of Earth’s Sahara Desert.
This image shows a slice of Utopia Planitia, the plain that fills this colossal and ancient basin.
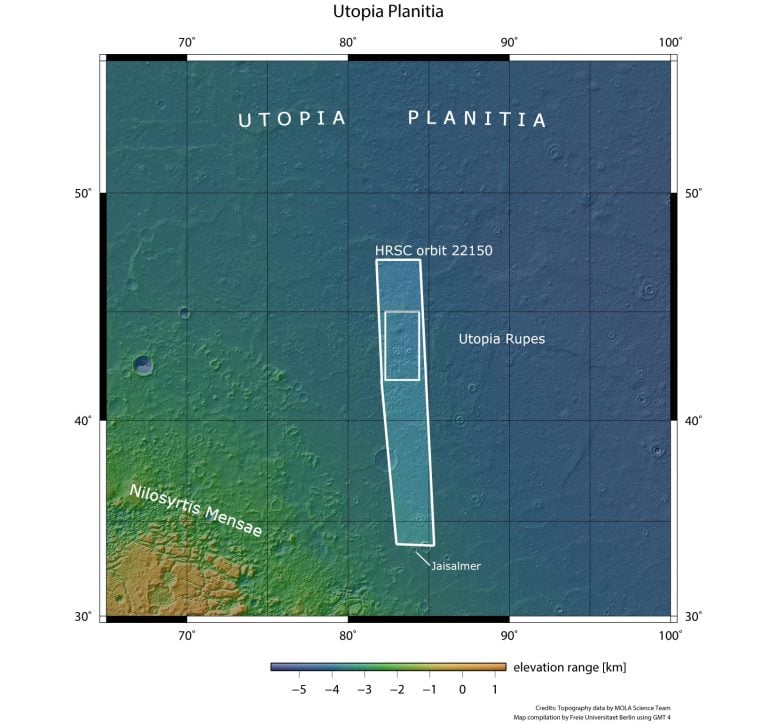
This image from ESA’s Mars Express shows Utopia Planitia, a plain that fills one of three major basins in the northern hemisphere of Mars – Utopia – and has a diameter of 3,300 km, in wider context. The area outlined by the bold white box indicates the area imaged by the Mars Express High Resolution Stereo Camera on July 12, 2021, during orbit 22150. Credit: NASA/MGS/MOLA Science Team
This plain is thought to have formed as the Utopia basin was filled by a mix of sediments, lavas, and volatile substances (those that vaporize easily, such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and water), all transported across the Martian surface by water, wind or other processes.
Layers of ice
Utopia Planitia is an intriguing and ice-rich region; ice has been spotted lying both at and just below the surface, and at greater depths (detected via observations of fresh craters and pits, and by probing Mars’ deeper layers using radar).
Visible to the left and right of this scene are large, smooth patches of surface known as ‘mantled deposits’. These are thick layers of ice- and dust-rich material that have smoothed the surface and were likely deposited as snow back when Mars’ rotational axis was much more tilted than it is today (as was last the case some 10 million years ago).
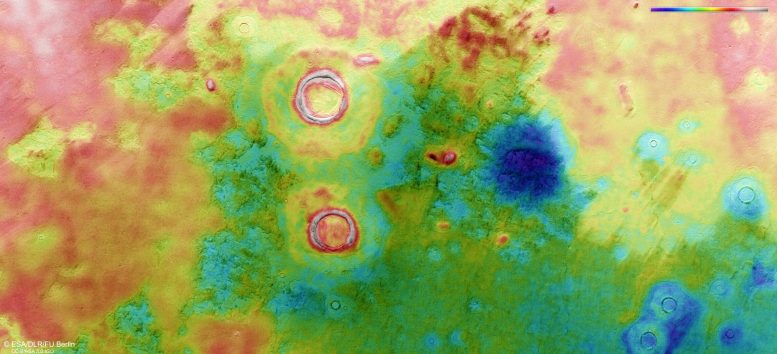
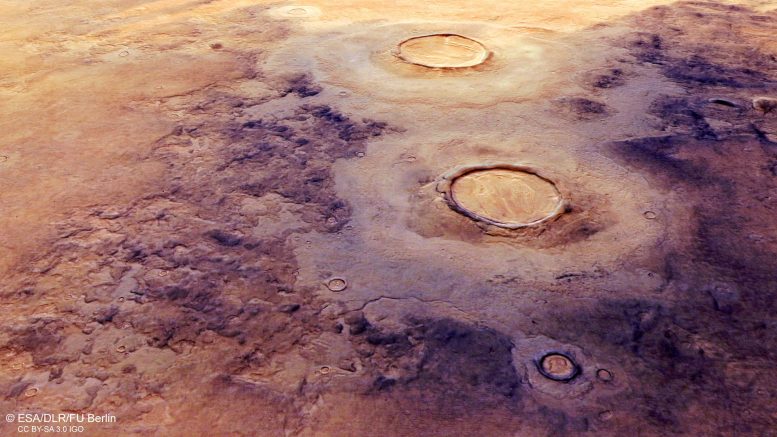
This color-coded topographic image of Utopia Planitia was created from data collected by ESA’s Mars Express on July 12, 2021. It is based on a digital terrain model of the region, from which the topography of the landscape can be derived. Lower parts of the surface are shown in blues and purples, while higher altitude regions show up in whites and reds, as indicated on the scale to the top right. North is to the right. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Moving back towards image center, the two largest impact craters visible here are surrounded by double-layered mounds of material. A similarly layered appearance is also visible in the deposits that have built up within the craters themselves, and in the craters’ thick rims.
Brain terrain
These craters are more interesting still. The second-largest crater in this image (just below-left of centre) showcases a texture known as ‘brain terrain’, where material has become deformed and warped in a concentric pattern that resembles the complex patterns and ridges found on the surface of the human brain.
Brain terrain is associated with the icy material found near the boundary between Mars’ northern plains and its southern highlands, a ‘dichotomy’ located to the south/south-west (upper left) of this scene.’

This oblique perspective view of Utopia Planitia on Mars was generated from the digital terrain model and the nadir and color channels of the High Resolution Stereo Camera on ESA’s Mars Express. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Just to the right of the brain-textured crater is an especially dark-colored region, created as the ice-rich ground contracted and cracked at low temperatures. This formed polygonal patterns and fractures that subsequently captured dark dust blown across Mars by wind, leading to the dark appearance seen here.
Additionally, scalloped depressions are omnipresent throughout this image. These have circular to elliptical shapes, depths of several tens of meters, and sizes varying from tens to thousands of meters across.
These features are the result of ground ice either melting or turning to gas, which then causes the surface to weaken and collapse. Upon closer look, layered mantled deposits can also be seen in and around these scalloped depressions.
Just to the right of the brain-textured crater is an especially dark-colored region, created as the ice-rich ground contracted and cracked at low temperatures. This formed polygonal patterns and fractures that subsequently captured dark dust blown across Mars by wind, leading to the dark appearance seen here.

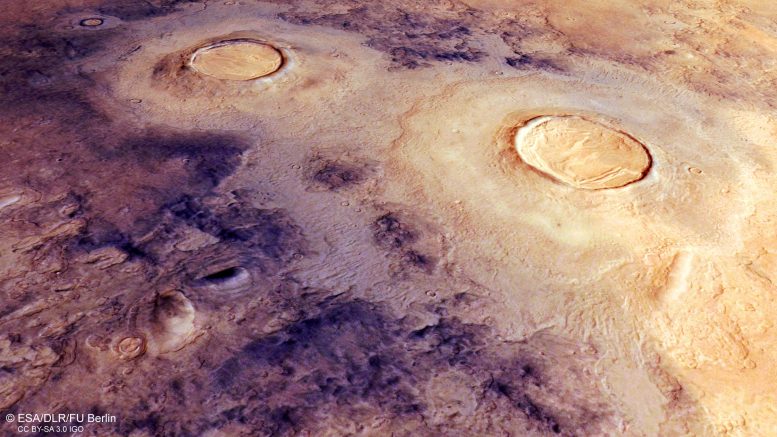
This oblique perspective view of Utopia Planitia on Mars was generated from the digital terrain model and the nadir and color channels of the High Resolution Stereo Camera on ESA’s Mars Express. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
Additionally, scalloped depressions are omnipresent throughout this image. These have circular to elliptical shapes, depths of several tens of meters, and sizes varying from tens to thousands of meters across.
These features are the result of ground ice either melting or turning to gas, which then causes the surface to weaken and collapse. Upon closer look, layered mantled deposits can also be seen in and around these scalloped depressions.
A diverse surface
Mars Express has been orbiting the Red Planet since 2003, imaging Mars’ surface, mapping its minerals, identifying the composition and circulation of its tenuous atmosphere, probing beneath its crust, and exploring how various phenomena interact in the martian environment.

This stereoscopic image shows Utopia Planitia on Mars, and was generated from data captured by the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) on ESA’s Mars Express orbiter on July 12, 2021 during orbit 22150. The anaglyph, derived from data acquired by the nadir channel and one stereo channel of the HRSC, offers a three-dimensional view when viewed using red-green or red-blue glasses. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
The mission’s High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC), responsible for these latest images, has revealed much about Mars’ diverse surface features, with recent image releases showing everything from wind-sculpted ridges and grooves to geologically rich regions filled with volcanoes, impact craters, tectonic faults, river channels and ancient lava pools. The camera has also captured other views of Utopia Planitia, such as a snapshot of Adamas Labyrinthus.

«Maven de internet exasperantemente humilde. Comunicadora. Fanático dedicado al tocino.»
También te puede interesar
-
Dormir bien el fin de semana puede reducir en una quinta parte el riesgo de sufrir enfermedades cardíacas: estudio | Cardiopatía
-
Una nueva investigación sobre la falla megathrust indica que el próximo gran terremoto puede ser inminente
-
Caso de Mpox reportado en la cárcel del condado de Las Vegas
-
SpaceX lanzará 21 satélites Starlink en el cohete Falcon 9 desde Cabo Cañaveral – Spaceflight Now
-
SpaceX restablece el lanzamiento pospuesto de Polaris Dawn, una misión espacial comercial récord

